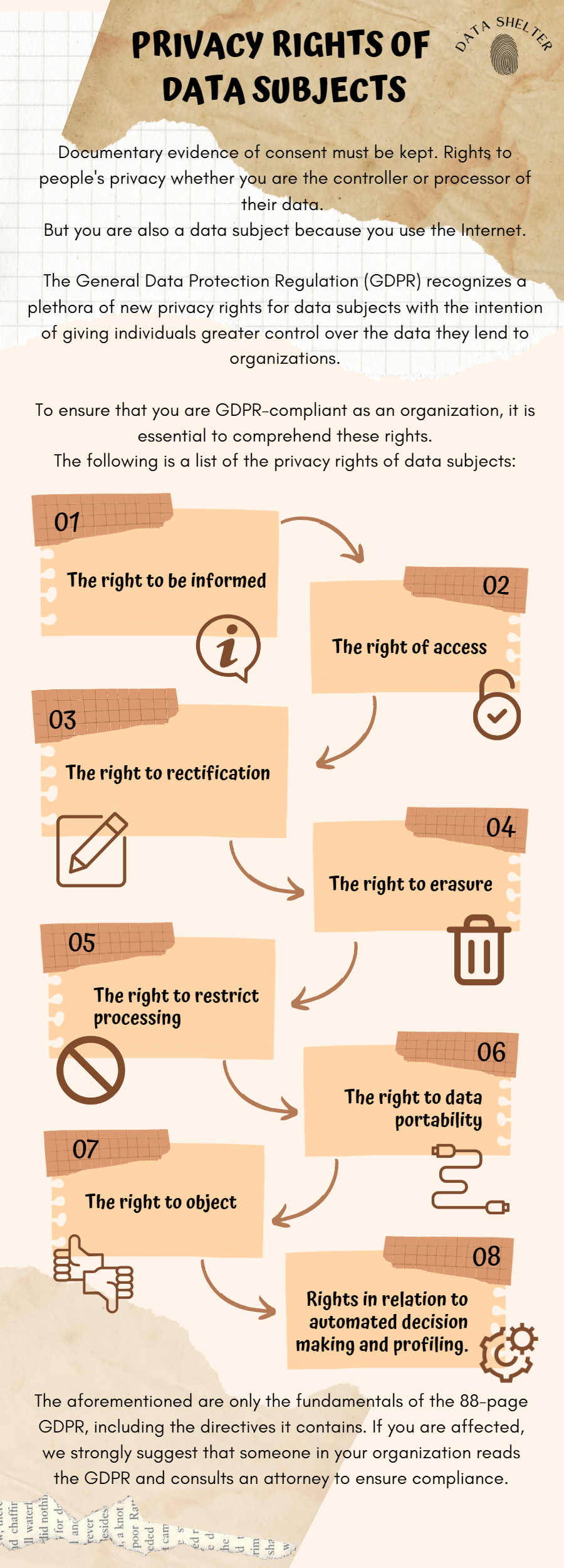
Material
According to the European Convention on Human Rights from 1950, "Everyone has the right to respect for his private and family life, his home, and his correspondence," the right to privacy is a fundamental human right. The European Union has sought to ensure the right's protection through legislation on this basis.
The strictest privacy and security law in the world is the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Even though it was drafted and approved by the European Union (EU), it imposes obligations on organizations worldwide as long as they target or collect data pertaining to EU citizens and individuals in Europe.
On May 25, 2018, the regulation went into effect.
At a time when more people are entrusting their personal data to cloud services and breaches occur on a daily basis, the goal of the GDPR was to demonstrate the EU's firm stance on data privacy and security.
GDPR compliance is a daunting prospect, particularly for small and medium-sized businesses (SMEs), due to the regulation's size, scope, and lack of specifics. With social media popping around the world now, Europe’s data protection authority declared the EU needed “a comprehensive approach on personal data protection”.
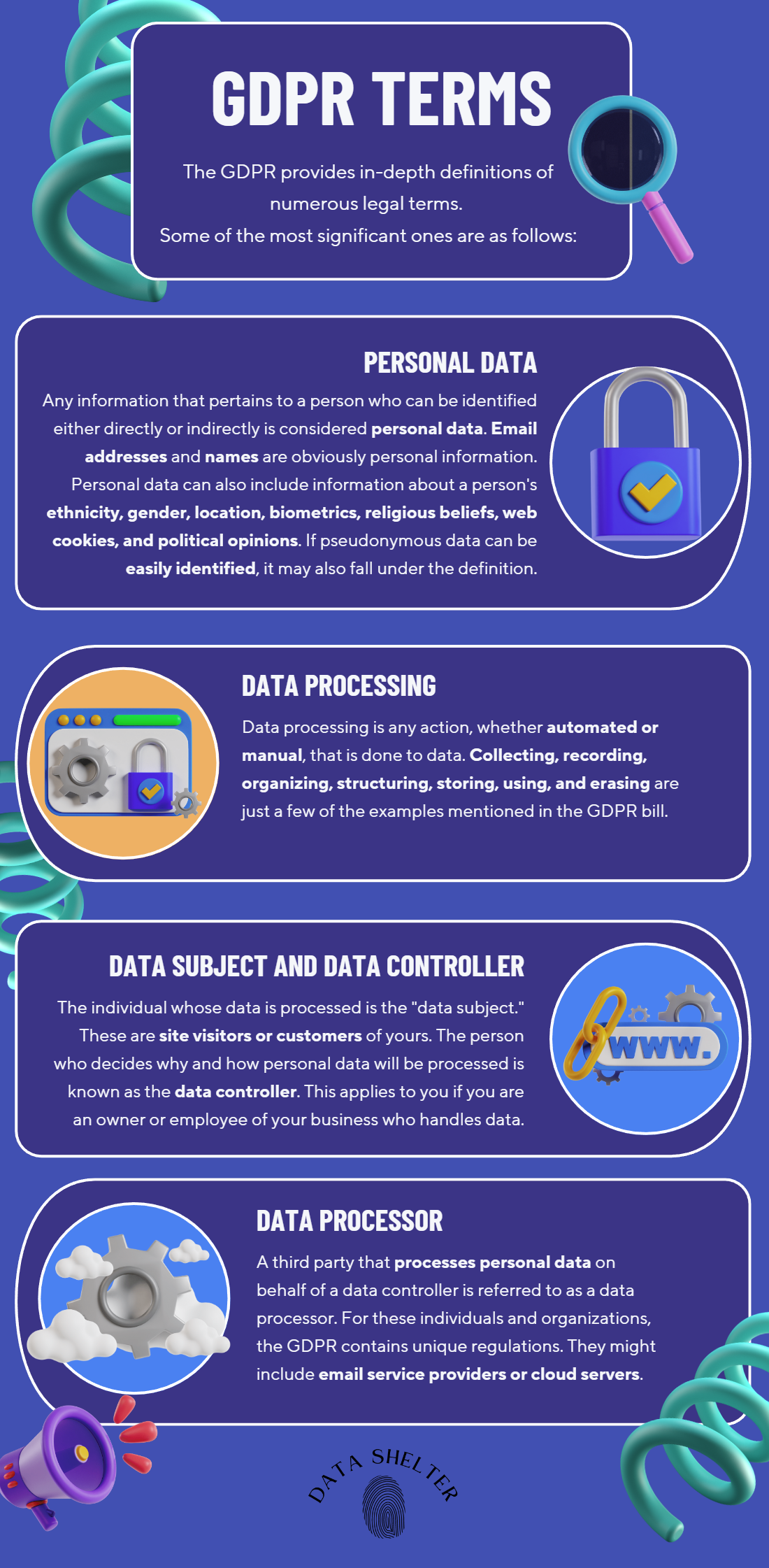


Data Security
You are required to use "appropriate technical and organizational measures" to handle data securely.
Technical measures can include signing a contract with cloud providers that use end to-end encryption or requiring your employees to use two-factor authentication on accounts where personal data are stored.
Employee training, including the inclusion of a data privacy policy in the handbook, and restricting access to personal data to only those employees who require it are examples of organizational measures. Policies such as do not open emails or attachments from suspicious emails or links. Or to not insert unknown USBs into work computers. Or to never give to customers other customer’s information UNLESS you contact them and ask for consent even if it is for the benefit of the both of them.
You have 72 hours to notify the data subjects of a data breach or face penalties. If you use technological safeguards, such as encryption, to render data inaccessible to an attacker, you may be exempt from this notification requirement.
Data protection by design and by default
Data security must now be a part of everything you do in your company "by design and by default." In practice, this means that when designing any new product or activity, you must take data protection principles into account. This idea is covered in Article 25 of the GDPR.
Let's say you're launching a brand-new app for your business. You need to consider the personal data that the app might possibly collect from users, as well as ways to reduce the amount of data collected and secure it using the most recent technology.

Consent